In today’s digital age, data mining is pivotal in extracting meaningful insights from vast amounts of information. Leveraging techniques from statistics, machine learning, and database systems, data mining identifies patterns, relationships, & trends in data to enable data-driven decisions, solve business challenges, and uncover hidden opportunities. Industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, & telecommunications rely heavily on data mining to stay competitive.
What is Data Mining?
Data mining refers to the systematic process of analyzing large datasets to discover useful patterns and knowledge. Unlike traditional data analysis, it focuses on uncovering hidden insights that are not immediately visible. This process involves transforming raw data into actionable intelligence. Common applications include customer profiling, market basket analysis, anomaly detection, and predictive modeling.

Understanding the Term “Data Mining”
The term “mining” traditionally refers to extracting valuable materials, such as coal or diamonds, from the earth. In computer science, “data mining” involves extracting valuable knowledge from data warehouses. Unlike physical mining, the end result isn’t more data but meaningful patterns and insights. Hence, data mining is a critical step in the broader process of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD).
Origins of Data Mining
The term “Knowledge Discovery in Databases” was introduced by Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro in 1989. Over time, “data mining” became the more widely accepted term, particularly in business and media circles. Today, data mining and knowledge discovery are often used interchangeably.
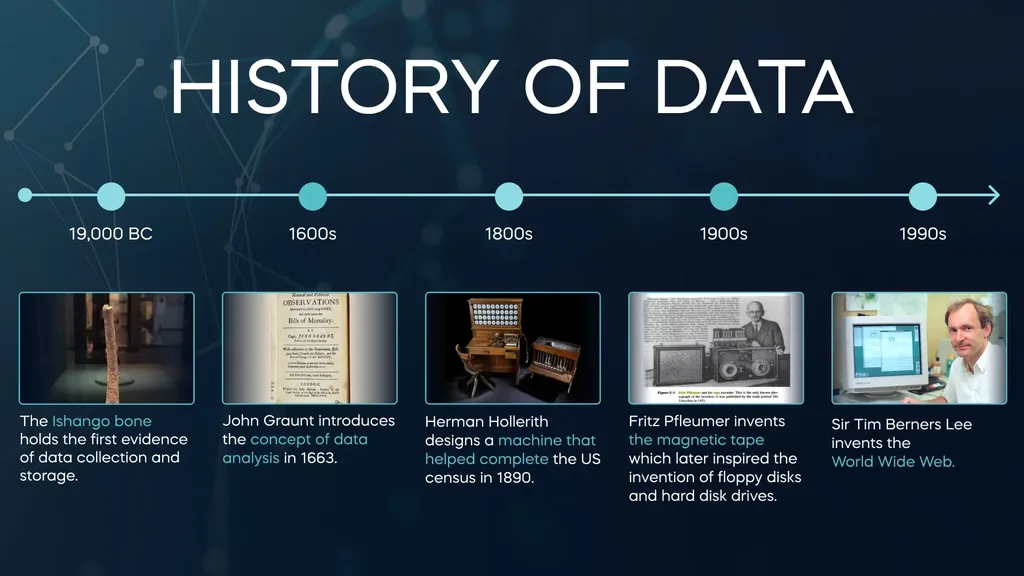
History of Data Mining
The history of data spans thousands of years, with key milestones marking its evolution:
- 19,000 BC: The Ishango bone holds the first evidence of data collection and storage.
- 1600s: John Graunt introduces the concept of data analysis in 1663.
- 1800s: Herman Hollerith designs a machine that helped complete the US census in 1890.
- 1900s: Fritz Pfleumer invents the magnetic tape, which later inspired the invention of floppy disks and hard disk drives.
- 1990s: Sir Tim Berners-Lee invents the World Wide Web, revolutionizing data sharing and access.
Why is Data Mining Important?
- Improved Decision-Making: Provides actionable insights to guide strategic decisions.
- Cost Efficiency: Helps businesses optimize operations and reduce waste.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Facilitates personalized products and services.
- Fraud Detection: Identifies anomalies to prevent fraudulent activities.
- Predictive Analytics: Anticipates trends and future events, empowering proactive actions.
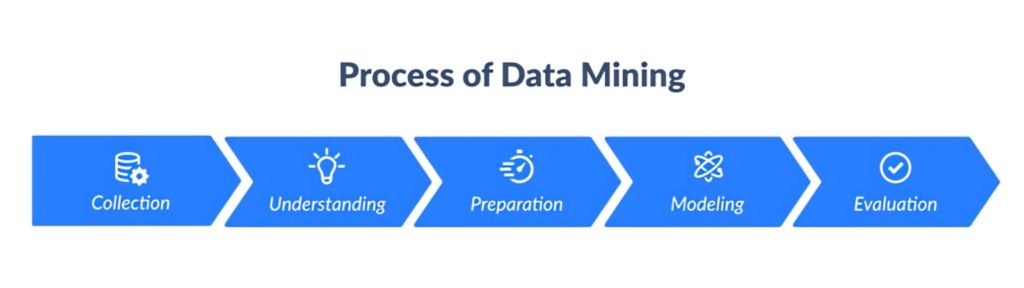
The Data Mining Process
The data mining workflow is typically divided into five main stages:
- Collection: Gathering raw data from various sources.
- Understanding: Interpreting the data to identify goals and objectives.
- Preparation: Cleaning, integrating, and transforming data to ensure accuracy.
- Modeling: Applying algorithms to uncover patterns and trends.
- Evaluation: Analyzing results and presenting findings in a comprehensible format.
Applications of Data Mining
- Financial Analysis: Detecting fraudulent activities and assessing risks.
- Healthcare: Predicting patient outcomes and identifying at-risk groups.
- Retail: Understanding customer purchasing habits for inventory optimization.
- Telecommunications: Analyzing customer churn and improving network services.
Real-Life Examples:
- Market Basket Analysis: Identifying items frequently purchased together, aiding promotional strategies.
- Protein Folding: Studying biological cells to predict protein interactions, helping in medical research.
- Fraud Detection: Analyzing unusual patterns in credit card transactions or mobile activity to flag fraudulent behavior.
Benefits of Data Mining
- Improved Decision-Making: Identifies patterns to support strategic initiatives.
- Increased Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks, saving time and resources.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Uncovers new opportunities and areas for improvement.
- Better Customer Insights: Helps tailor products and services to customer needs.
- Risk Management: Identifies potential risks by analyzing behavior and market conditions.
Challenges in Data Mining
- Data Privacy: Ensuring sensitive information is protected during analysis.
- Data Quality: Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to unreliable results.
- Scalability: Managing and processing ever-growing datasets efficiently.
- Interpretability: Ensuring that findings are easy to understand and actionable.
Future of Data Mining
As artificial intelligence and big data technologies evolve, data mining is becoming more advanced. Future trends include real-time data analysis, integration with IoT devices, and automated predictive analytics, ensuring data mining remains an indispensable tool for businesses.
Conclusion
Data mining is a cornerstone of modern analytics, enabling organizations to transform raw data into strategic insights. By understanding its processes and applications, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data, ensuring innovation and competitiveness in a rapidly evolving world. Mastering data mining techniques is essential for staying ahead in today’s data-driven landscape.